Melting Point C Physical Form. Phosphorus pentoxide reacts violently with the following.
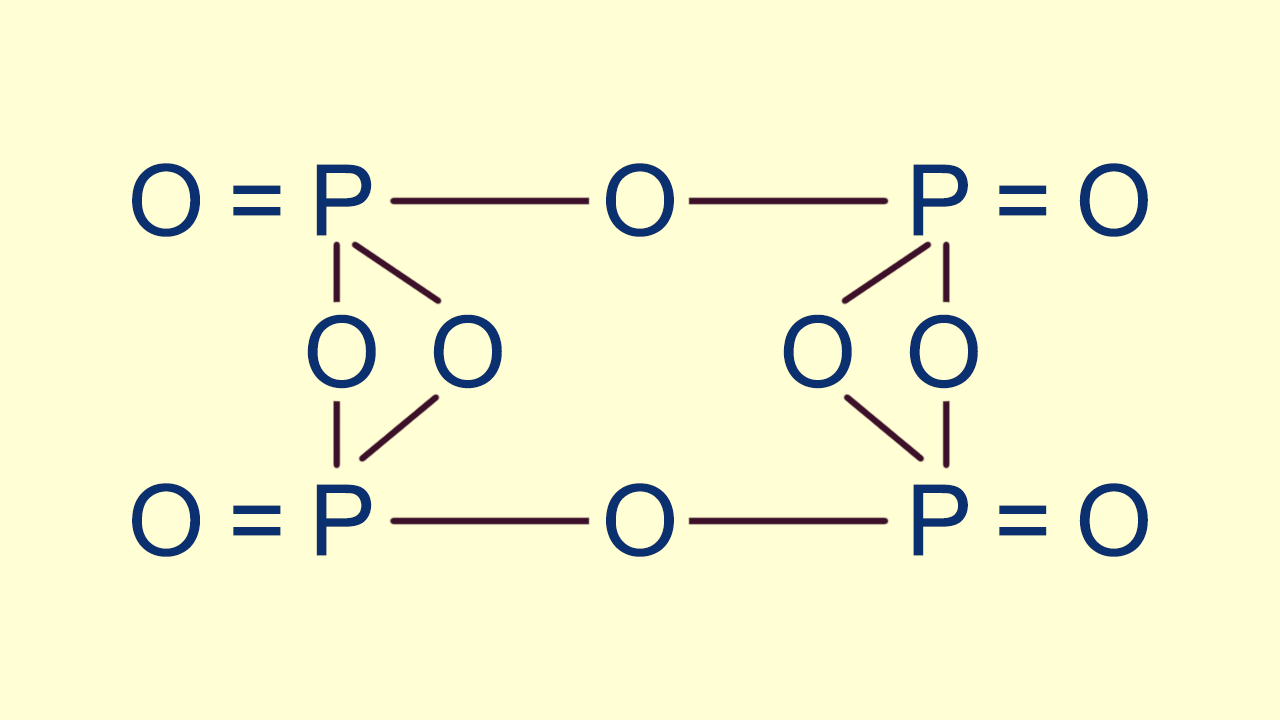
P 4 O 6 is a molecular formula.
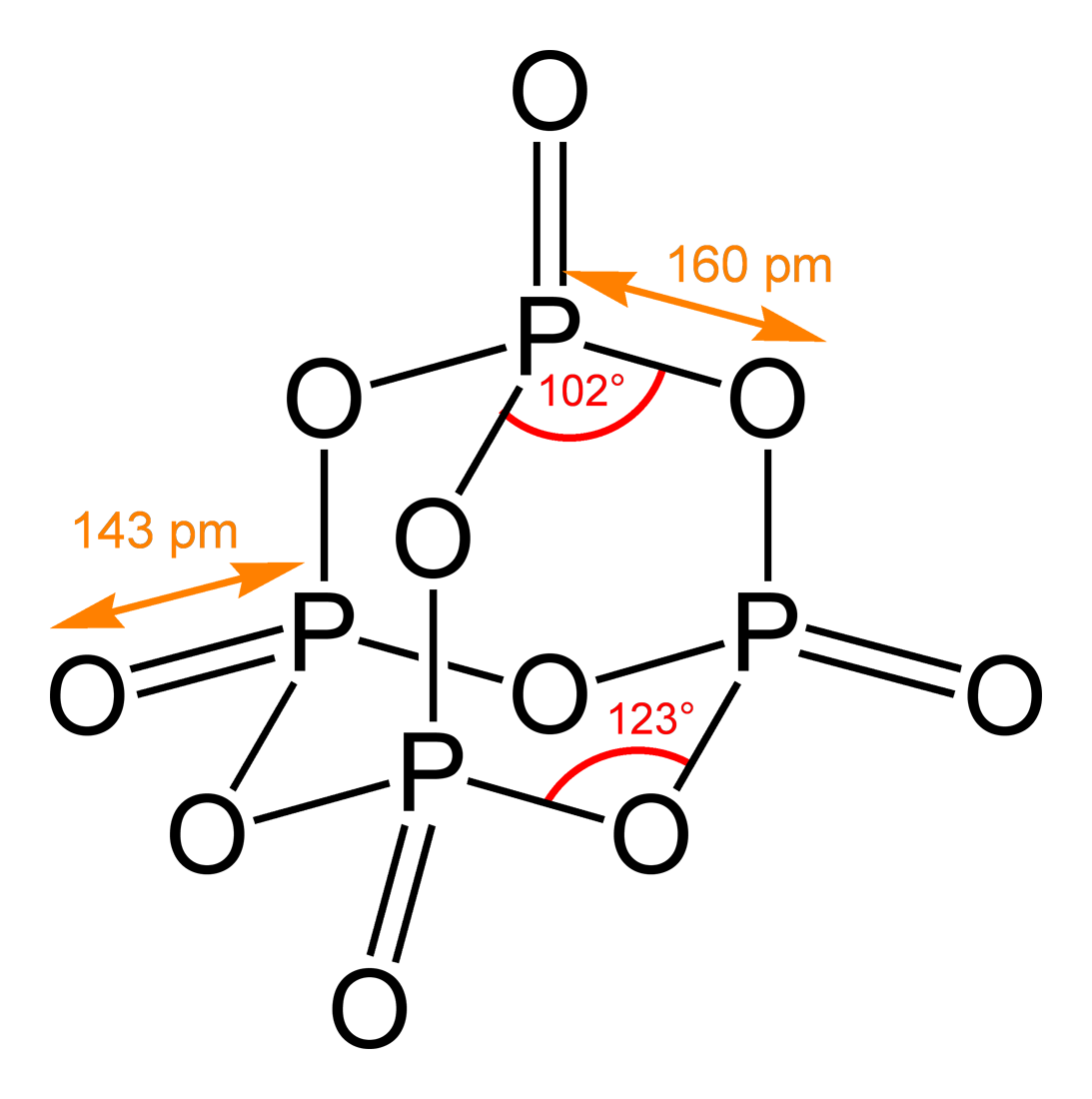
Formula for phosphorus pentoxide. Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P 4 O 10 with its common name derived from its empirical formula P 2 O 5. This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent.
Phosphorus pentoxide crystallizes in at least four forms or polymorphs. The most familiar one a metastable form shown in. Phosphorus pentoxide reacts violently with the following.
Ammonia hydrofluoric acid oxygen difluoride potassium sodium propargyl alcohol calcium oxide sodium hydroxide and chlorine trifluoride. A violent explosion occurs if a solution of perchloric acid in chloroform is poured over phosphorus pentoxide. Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P 4 O 10 with its common name derived from its empirical formula P 2 O 5.
This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent. Phosphorus pentoxide Phosphorous acid.
Except where otherwise noted data are given for materials in their standard state at 25 C 77 F 100 kPa. What is Infobox references. Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P 4 O 6.
Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexoxide the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of. O 10 P 4. Tetraphosphorus decaoxide is a phosphorus oxide.
1 Structures Expand this section. 2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. Tetra is a prefix that is used for naming four atoms of a formulas nonmetal element.
P 4 O 6 is a molecular formula. Its empirical formula is P 2 O 3. Tetraphosphorus hexoxide is also called phosphorus trioxide.
A binary covalent compound is composed of two different elements usually nonmetals. For example a molecule of chlorine trifluoride ClF 3 contains 1 atom of chlorine and 3 atoms of fluorine. N 2 O 5.
N 2 O 3. C 2 H 5 OH. 83 Iron oxide formula.
Fe 2 O 3. C 2 H 6 O 2. Al 2 S 3.
Ammonium carbonate formula NH 4 2 CO 3. Ammonium nitrate formula NH 4NO 3 90. For each of the following questions determine whether the compound is ionic or covalent and write the appropriate formula for it.
11 dinitrogen trioxide N2O3. 14 lithium acetate LiC2H3O2. 15 phosphorus trifluoride PF3.
16 vanadium V oxide V2O5. 17 aluminum hydroxide AlOH3. Formula writing rules to write the correct chemical formulas for each compound.
Compound Name Type of Compound. Ionic or Covalent Chemical Formula 1 copper II chlorite 2 sodium hydroxide 3 nitrogen dioxide 4 cobalt III oxalate 5 ammonium sulfide 6 aluminum cyanide 7 carbon disulfide 8 tetraphosphorous pentoxide 9 potassium permanganate 10 manganese III chloride Compound. Phosphorus will spontaneously ignite if exposed to air.
Phosphorus ignites at approximately 86F 30C in air. The ignition temperature is higher when the air is dry. Phosphorus reacts violently with oxidants halogens some metals nitrites sulfur and many other compounds causing a fire hazard.
Phosphorus Pentoxide P4O10 Phophorus Pentoxide P4S3 Phosphorus Sesquisulfide PbC2H3O22 LeadII Acetate PbC2H3O24 LeadIV Acetate PbNO32 LeadII Nitrate PbCl2 LeadII Chloride PbCl4 LeadIV Chloride PbCrO4 LeadII Chromate PbI2 LeadII Iodide PbO LeadII Oxide PbO2 LeadIV Oxide PBr3 Phosphorus Tribromide PbS LeadII Sulfide PCl3. Empirical Formula Hill Notation. C 25 H 42 N 7 O 17 P 3 S xLi CAS No.
83762 free acid basis Compare Product No. Ac-CoA Synthase Inhibitor - CAS 508186-14-9 - Calbiochem. Ac-CoA Synthase Inhibitor - CAS 508186-14-9 - Calbiochem.
Melting Point C Physical Form. Analytical 63 ACS reagent 44 Puriss 35 Cell Culture 21 Reagent 18 Purum 17 Anhydrous 13 BioXtra 13 ReagentPlus 11 Plant 7 Show More.