An antidote is a drug chelating substance or a chemical that counteracts neutralizes the effects of another drug or a poison. There are dozens of different antidotes.

However some may only counteract one particular drug whereas others such as charcoal may help reduce the toxicity of numerous drugs.
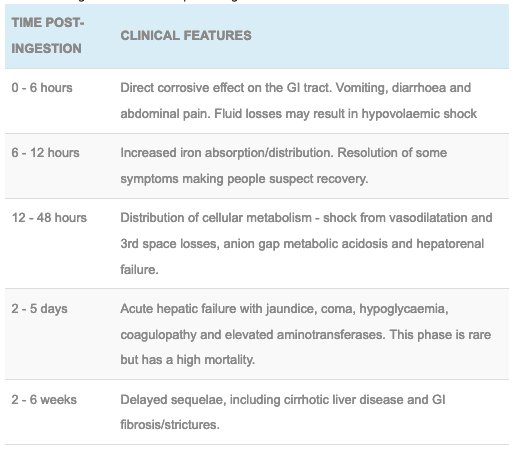
Iron toxicity antidote. A specific antidote desferioxamine is available. Iron has local gastrointestinal effects followed by systemic effects that do not occur without preceding GI toxicity following iron ingestion Local effects. Corrosive injury to the gastrointestinal mucosa resulting in vomiting diarrhoea haemetemesis melaena and fluid losses that may result in hypovolaemia.
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον pharmakon antidoton medicine given as a remedyAntidotes for anticoagulants are sometimes referred to as reversal agents. The antidotes for some particular toxins are manufactured by injecting the toxin into an animal in small doses.
A cyanide is a chemical compound that contains the group CN. This group known as the cyano group consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. In inorganic cyanides the cyanide group is present as the anion CN Soluble salts such as sodium cyanide and potassium cyanide are highly toxic.
Hydrocyanic acid also known as hydrogen cyanide or HCN is a highly volatile. Ferrous sulfide is occasionally formed unintentionally when materials containing sulfur are treated in iron and steel vessels- eg in petroleum refineries. If the plant is opened and the deposit of ferrous sulfide is exposed to air its exothermic oxidation may raise temp of gases and vapors in the vicinity.
Because iron has been shown to increase the in vitro toxicity of amyloid-beta the present study was undertaken to determine whether iron can make amyloid-beta neurotoxic in vivo. Amyloid-beta and 10 mM iron as ferric ammonium citrate were coinjected into rat cerebral cortex and the neuronal loss was compared with that produced by pure amyloid-beta or pure iron. An antidote is a drug chelating substance or a chemical that counteracts neutralizes the effects of another drug or a poison.
There are dozens of different antidotes. However some may only counteract one particular drug whereas others such as charcoal may help reduce the toxicity of numerous drugs. Most antidotes are not 100 effective and fatalities may still occur even when an.
No specific antidote for Lithium poisoning is known. Mild symptoms of Lithium toxicity can usually be treated by reduction in dose or cessation of the drug. In severe cases of Lithium poisoning the goal of treatment is elimination of this ion from the patient.
Administration of gastric lavage should be performed but use of activated charcoal is not recommended as it does not significantly. Ethylene glycol exposures can cause varying degrees of toxicity and management generally requires supportive care close laboratory monitoring and antidote therapy. The primary treatments are either ethanol or fomepizole and occasionally dialysis.
1 Ethylene glycol C2H6O2 is a toxic alcohol that is found in various household and industrial agents. The term toxic alcohols is a. Renal damage in cadmium toxicity.
Dimercaprol British anti- Lewisite BAL is efficient antidote in heavy metal poisoning. BAL and their analogues meso-2 3-dimercaptosuccinic acid DMSA and 2 3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid DMPS are used as antidote course of therapy for heavy metal poisoning. BAL must be administered in the first 4 hours of poisoning.
Antidote and other Elixirs Tap News Weaver Intro by Dr. Ariyana Love Our Elixirs Updated. June 24 2021 Front line doctors and medical experts dropped a bombshell in late April 2021 revealing matters of national security for all nation states.
Transmission between the Covid-19 vaxxed and unvaxxed is causing Adverse Reactions in.