
Patients who have aspirin toxicity can have a myriad of symptoms. In the case of anti-infective drug development the information permits anticipation of problems relating to clinical safety.
Aspirin is an orally administered non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent.
Mechanism of toxicity aspirin. Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action Inflamm Res. The same side effects including gastric and renal toxicity. Recent research has shown that there are at least two COX isoenzymes.
COX-1 is constitutive and makes PGs that protect the stomach and kidney from damage. COX-2 is induced by inflammatory stimuli such as cytokines and produces PGs that contribute to. Elucidating the mechanism of action of novel drugs and medications is important for several reasons.
In the case of anti-infective drug development the information permits anticipation of problems relating to clinical safety. Drugs disrupting the cytoplasmic membrane or electron transport chain for example are more likely to cause toxicity problems than those targeting. Acute oral LD50 values have been reported as over 10 gkg in humans cats and dogs 092 gkg - 148 gkg in albino rats 119 gkg in guinea pigs 11 gkg in mice and 18 gkg in rabbit models Label.
Salicylate toxicity is a problem that may develop with both acute and chronic salicylate exposure 7. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever.
Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis which normally protect against nephrotoxicity.
Aspirin increases toxicity of triamterene by pharmacodynamic antagonism. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis increasing the risk of nephrotoxicity. Mechanism of Action.
Aspirin is a cyclooxygenase-1 COX-1 inhibitor. It is a modifier of the enzymatic activity of cyclooxygenase-2. Patients who have aspirin toxicity can have a myriad of symptoms.
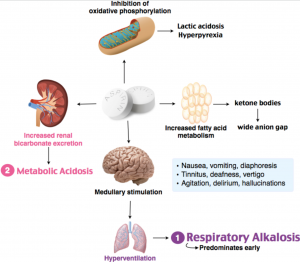
Symptoms of mild toxicity can be but are not limited to tinnitus dizziness lethargy nausea and vomiting. For more severe toxicity the signs and symptoms include hyperthermia tachypnea. Swallowing oil of wintergreen is like swallowing a large number of adult aspirin.
Tea tree oil is used for some kinds of fungal skin infections. Nutmeg is used in food but when misused or abused can cause hallucinations and coma. Eucalyptus is used for its soothing effects when inhaled for example during a cold or cough.
Aspirin is an orally administered non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent. Acetylsalicylic acid binds to and acetylates serine residues in cyclooxygenases resulting in decreased synthesis of prostaglandin platelet aggregation and inflammation. This agent exhibits analgesic antipyretic and anticoagulant properties.
Synthesis of Aspirin By. To determine which of four catalysts yields the fastest reaction rate in the acetylation of salicylic acid 1 to form acetylsalicylic acid 2. Aspirin Synthesis Tap water was heated on a steam bath in a 250 mL beaker.
The temperature of an alcohol thermometer was equilibrated in a beaker of room temperature tap water. Mechanism of Action. The main mechanism of action of NSAIDs is the inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase COX.
Cyclooxygenase is required to convert arachidonic acid into thromboxanes prostaglandins and prostacyclins. The therapeutic effects of NSAIDs are attributed to the lack of these eicosanoids. Specifically thromboxanes play a role.
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NSAID. Other examples of drugs in this class include aspirin and diclofenac. Taken together these drugs are all pain relievers that are used.
Possibly through inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-3 COX-3 Decreases synthesis of prostaglandins. Antipyresis through inhibition of hypothalamic heat center. A - Rapid and near complete absorption.
D - Vd 095 Lkg. M - T 12 15-2 hrs 40-60 - Glucuronidation. 5-10 - Metabolism through CYP450CYP2E1 Forms.
Increased levels of lithium may lead to lithium toxicity. Aspirin may reduce the blood pressure lowering effects of blood pressure medications. This may occur because prostaglandins have a role in the regulation of blood pressure.
When aspirin is used in combination with methotrexate Rheumatrex Trexall or aminoglycoside antibiotics for example gentamicin the blood levels of the. The ototoxic effects of quinine are very similar to aspirin and the toxic effects are usually reversible once medication is discontinued. The signs of ototoxicity in order of frequency are.
1 Development of tinnitus in one or both ears. 2 Intensification of existing tinnitus or the appearance of a new sound. 3 Fullness or pressure in the ears other than being caused by infection.
Are more susceptible to drug toxicity and drug-to-drug interactions. Careful monitoring of liver and kidney function is important for this age group. Therapy is always started at the lowest level possible and adjusted accordingly.
15 min 12 h Metabolism. The probable mechanism of action is to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis rather than simply to provide analgesia. The ibuprofen in MOTRIN tablets is rapidly absorbed.
Peak serum ibuprofen levels are generally attained one to two hours after administration. With single doses up to 800 mg a linear relationship exists between amount of drug administered and the integrated area under the serum.