
106-108 The pH hypothesis. It can be manufactured synthetically and it used as a fragrance in foods beverages and liniments.
See Differential diagnosis below This topic review will discuss the diagnosis and management of isopropyl alcohol intoxication.
Salicylate intoxication acidosis. Patients with mild intoxication frequently have nausea and vomiting abdominal pain lethargy ringing in the ears and dizziness. More significant signs and symptoms occur in more severe poisonings and include high body temperature fast breathing rate respiratory alkalosis metabolic acidosis low blood potassium low blood glucose hallucinations confusion. Salicylate Toxicity This review focuses on risk factors for salicylate poisoning the pathophysiology of both acute and chronic toxicity hidden sources of salicylate that may result in.
Indications for hemodialysis include severe acidosis or hypotension despite fluid resuscitation. Salicylate levels are greater than 100 mgdL mechanical ventilation or end-organ damage. Common signs of end-organ damage in salicylate toxicity include seizures rhabdomyolysis pulmonary edema cerebral edema and renal failure.
Hemodialysis removes salicylates and lactate which should. High anion gap acidosis occurs in diabetic ketoacidosis. Severe malnutrition or starvation alcoholic lactic acidosis.
High-fat low-carbohydrate dietslipid administration. Poisoning eg salicylate intoxication after initial stage. And drug therapy eg acetazolamide Diamox NH 4 Cl.
Lactic acidosis diabetic ketoacidosis renal insufficiencyuremia. Salicylate intoxication ethanol intoxication methanol intoxication ethylene glycol intoxication a component of antifreeze products Further evaluation. Delta ratio anion gap - 12 24 - HCO 3- 7.
Methyl salicylate oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil is an organic ester naturally produced by many species of plants particularly wintergreens. The compound was first extracted and isolated from plant species Gaultheria procumbens in 1843. It can be manufactured synthetically and it used as a fragrance in foods beverages and liniments.
It forms a colorless to yellow or reddish liquid. This is especially true in certain forms of metabolic acidosis. For example in high anion gap acidosis secondary to accumulation of organic acids lactate and ketones these anions are eventually metabolized to HCO 3-When the underlying disorder is treated the serum pH corrects.
Thus caution should be exercised in these patients when providing alkali to raise the pH much higher than 720. Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the bodys acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes.
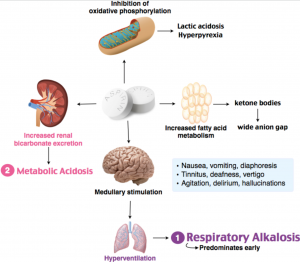
Increased acid production loss of bicarbonate and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids. Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 735. The most characteristic acid-base disorder generated by salicylate intoxication is mixed HAGMA and respiratory alkalosis.
Toxic salicylate levels directly stimulate the medullary respiratory center increasing both the rate and depth of respirations. This generates the respiratory alkalosis. Salicylate toxicity also uncouples oxidative phosphorylation inhibits citric acid cycle dehydrogenases.
Unlike for example non-anion-gap metabolic acidosis where most causes are not life threats. Causes of elevated anion gap back to contents ketoacidosis. Occurs when GFR.
Uncomplicated uremia rarely causes bicarbonate to fall below 12-15 mM or anion gap to increase. Renal tubular acidosis. Chronic renal failure.
Respiratory diseases that involve hyperventilation blowing off carbon dioxide and the development of alkalosis In people who are not vegetarians the pH of urine tends to be acidic. A diet rich in citrus fruits legumes and vegetables raises the pH and produces urine that is more alkaline. Most of the bacteria.
In patients with salicylate intoxication the beneficial effects of sodium bicarbonate are mediated by the production of metabolic alkalosis that decreases the amount of lipid soluble salicylate and driving the above reaction to the left resulting in decreased penetration into central nervous system and in increased urinary clearance. As was discussed above IV sodium bicarbonate may have. Ethanol b or ethylene glycol b intoxication.
A Most common causes of metabolic acidosis with an elevated anion gap b Frequently associated with an osmolal gap. Will have increase in Cl- GI loss of HCO 3 -. Metformin amplifies the degree of lactic acidosis but its not the sole cause of the illness.
Risk factors include renal insufficiency higher doses of metformin and alcoholism. Metformin-unrelated lactic acidosis MULA Metformin is an innocent bystander. Metformin levels are low.
Clinically it may be impossible to differentiate this from MALA. Lactic acidosis Methanol intoxication Paraldehyde ingestion Rhabdomyolysis Salicylate intoxication Uremia. Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetic Ketoacidosis and.
Isopropyl alcohol does not cause an elevated anion gap acidosis retinal toxicity as does methanol or renal failure as does ethylene glycol although it does increase the osmol gap. See Differential diagnosis below This topic review will discuss the diagnosis and management of isopropyl alcohol intoxication. Major In general avoid use of mannitol and salicylates.
Concomitant administration of nephrotoxic drugs such as the salicylates increases the risk of renal failure after administration of mannitol. However mannitol promotes the urinary excretion of salicylates and may be used as an adjunct in salicylate intoxication. Salicylate intoxication Anion gap 未測知陰離子已測知陰離子未測知陽離子已測 知陽離子 AG 未測知陰離子-未測知陽離子 已測知陽離子-已測知陰離子 Na-ClHCO3 已測知陽離子NaK 已測知陰離子ClHCO3 未測知陽離子MgAlCaCu 未測知陰離子proteinphosphate.
陰離子差距 Anion Gap Concept 定義. Following a period of CNS depressionmetabolic acidosis and cardiopulmonary symptoms become prominent although co-ingestion of ethanol will. In addition metabolic acidosis with normal or high arterial pH normal or reduced hydrogen ion concentration is usual in adults and children over the age of four years as a result of the presence of salicylate.
In children aged four years or less a dominant metabolic acidosis with low arterial pH raised hydrogen ion concentration is common. Since younger children are often not seen until. Respiratory acidosis ensues due to suppression of the respiratory centre.
In addition metabolic acidosis occurs as a result of the presence of salicylate. Since younger children are often not seen until they have reached a late stage of intoxication they are usually in the stage of acidosis. Generally the clinical severity of poisoning is less below a plasma-salicylate concentration of 500 mglitre 36 mmollitre unless there is evidence of metabolic acidosis.
Activated charcoal can be given within 1 hour of ingesting more than 125 mgkg of aspirin. Fluid losses should be replaced and intravenous sodium bicarbonate may be given ensuring plasma-potassium concentration is. Salicylate is the main form of AAS in the body and produces multiple alterations.
Initially the stimulation of the ventilatory center promotes a respiratory alkalosis. Then the mitochondrial dysfunction induced by sali-cylate will generate a progressive metabolic acidosis due to the accumulation of ketoacids lactic acid and dicarboxylic acids among others. Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a lower pH and decreased HCO 3- causing the blood to be too acidic for proper metabolickidney function.
Causes include diabetes shock and renal failure. Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated pH and increased HCO 3 and is seen in hypokalemia chronic vomiting losing acid from the stomach and sodium bicarbonate overdose. Salicylate dimethadione metabolites of halothane trichloroacetic acid and methoxyethanol methoxyacetic acid and acidic thalidomide metabolites also accumulate in the early rodent embryo see Table 20-3.
82 It has been hypothesized that acidic metabolites formed by hydrolysis of thalidomide within the embryo may be trapped there because of their high polarity. 106-108 The pH hypothesis.