The therapeutic range for free carbamazepine is 05 - 40 ugmL. To understand why a urea and electrolytes blood test is important it is best to know the basics of.
Please read our Terms Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about.
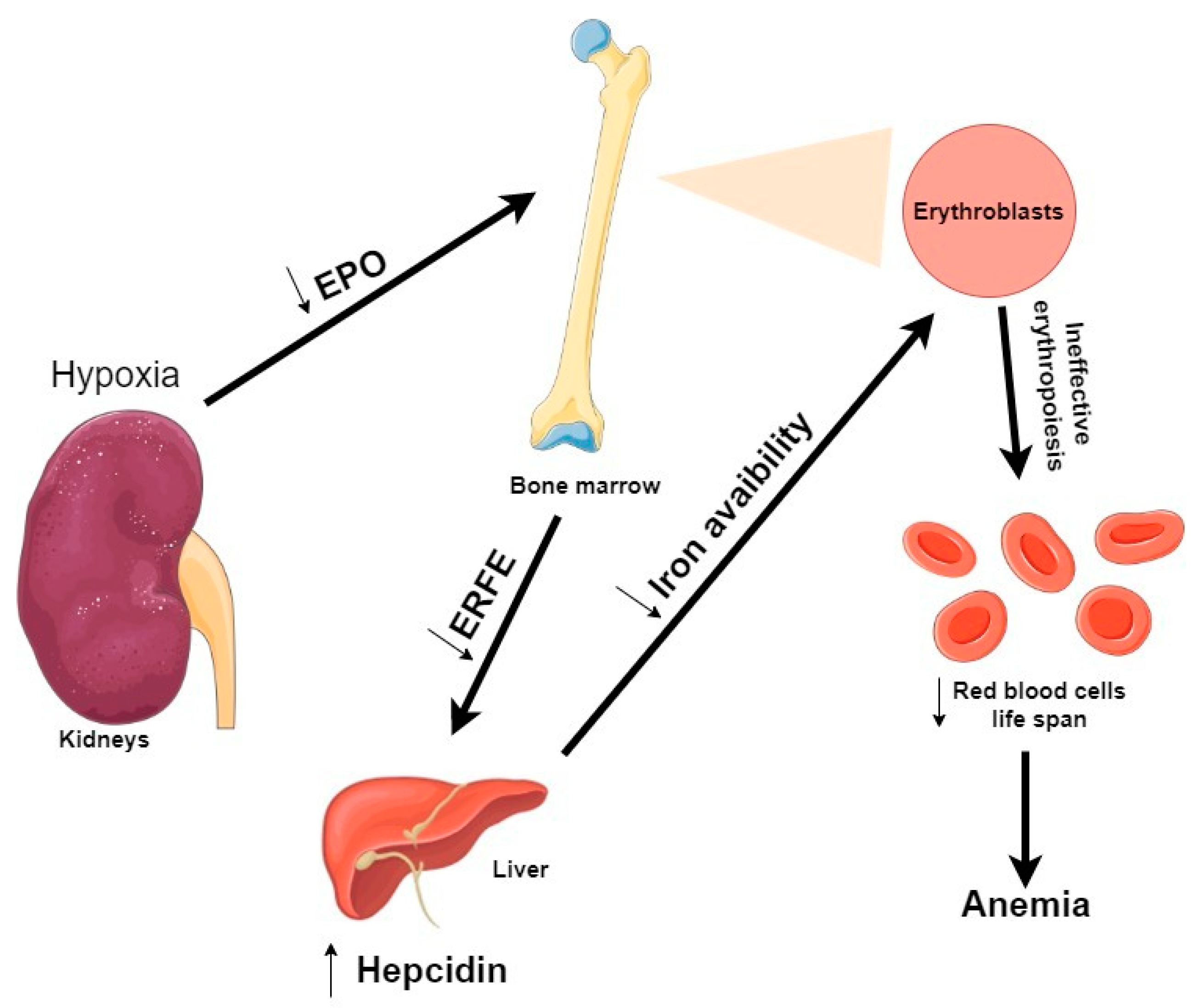
What is toxicity of the blood uremia. Uremia is the condition of having high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products such as urea and creatinine in the blood that would be normally excreted in the urine.
Uremic syndrome can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure also called renal. If left untreated uremia can lead to seizure coma cardiac arrest and death. When the body is unable to process or eliminate ammonia such as in protein toxicity will lead to the build up of ammonia in the bloodstream causing a condition called hyperammonemia.
Symptoms of elevated blood ammonia include muscle weakness and fatigue. In severe uremia carbamazepine may be displaced from protein resulting in a higher free fraction of circulating drug. Since neurologic activity and toxicity are directly related to the free fraction determination of free carbamazepine levels may be useful in adjusting dosage for uremic patients.
The therapeutic range for free carbamazepine is 05 - 40 ugmL. Levels 40 ugmL may be. Significant iron toxicity can result in a severe lactic acidosis from hypoperfusion due to volume loss vasodilation and negative inotropin effects.
Iron Toxicity Stages Staging Clinical Effect Time Frame. Nausea and vomiting abdominal pain diarrhea. 30 mins-6 hours Stage 2.
6-24 hours Stage 3. Shock and metabolic acidosis. An excess of nitrogen compounds in the blood may lead to uremia.
The serum Creatinine cree-AT-in-een is present after the chemical Creatine cree-uh-TEEN is broken down by the body in order to make energy for your muscles. The kidneys are normally able to filter out large amounts of creatinine on a daily basis. However when kidney problems are present your creatinine.
Anticholinergic toxicity is common in the emergency department but rarely fatal1 According to the 2015 annual American Association of Poison Control Centers AAPCC report there were just under 14000 exposures reported to poison control centers that year none of which lead to mortality1 However in prior years up to 51 cases have been reported as deadly234 Overdoses. Arterial blood gas analysis is essential as other causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis may include uremia methanol poisoning diabetic ketoacidosis acetaminophen toxicity aspirin toxicity and lactic acidosis. Sedative-hypnotics drugs can cause respiratory depression especially if ingested with opioids.
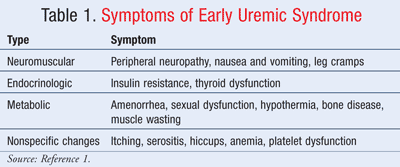
The common causes of cerebral edema include neoplasm intracranial hemorrhage. Nerve Problems Due to Uremic Toxicity. People with CKD may also suffer from neurological changes that can cause itching.
Toxins from excess uremia can enter the central nervous system and damage nerve cells. This damage may increase the perception of itch no matter the size of the rash. Peak blood levels of isoniazid are reached one to two hours after ingestion although toxic effects can begin to appear much sooner3 The drug readily diffuses to all body fluids and tissues with.
Blood samples were collected from the tail vein 15 and 30 min and 1 2 4 6 8 12 24 48 and 72 hr after dosing in order to measure radioactivity. After the initial absorption a biphasic decrease in the blood concentration of radiolabel was seen with half-time values for the biphasic decrease of about 2 and 20 hr respectively. How is the Specimen Collected for Iron Saturation Blood Test.
Following is the specimen collection process for Iron Saturation Blood Test. Blood Process of obtaining a blood sample in adults. A band is wrapped around the arm 3-4 inches above the collection site superficial vein that lies within the elbow pit The site is cleaned with 70 alcohol in an outward spiral away.
Heptanal is an n-alkanal resulting from the oxidation of the alcoholic hydroxy group of heptan-1-ol to the corresponding aldehyde. An endogenous aldehyde coming from membrane lipid oxidation it is found in the blood of lung cancer patients and has been regarded as a potential biomarker of lung cancer. This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience.
Please read our Terms Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about. Blood and urine tests are among the most commonly requested laboratory tests. These tests provide useful information about many aspects of your health.
To understand why a urea and electrolytes blood test is important it is best to know the basics of. Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases ABGs David A. Kaufman MD Chief Section of Pulmonary Critical Care Sleep Medicine Bridgeport Hospital-Yale New Haven Health Assistant Clinical Professor Yale University School of Medicine Section of Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Introduction.
Interpreting an arterial blood gas ABG is a crucial skill for physicians nurses respiratory. Because phenytoin is highly protein bound and only unbound drug is capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier to exert its pharmacologic effect unbound free phenytoin levels may be more clinically relevant than total levels to maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity. Although unbound free phenytoin levels can be measured by a laboratory assay this method may not be available on.
Normocytic anemias may be thought of as representing any of the following. A decreased production of normal-sized red blood cells eg anemia of. Made in the pancreas glucose helps to raise blood glucose levels if they are low and insulin helps to lower blood glucose levels if they are highNormally glucagon begins to act when blood glucose levels are low.
It causes the liver to change glycogen stored glucose to glucose. This glucose then travels to the bloodstream so the cells can use it for energy. Glucagon also stops the liver.